Quick Sort Algorithm. QuickSort is one of the most efficient sorting algorithms and is based on the splitting of an array into smaller ones.
How QuickSort Works?
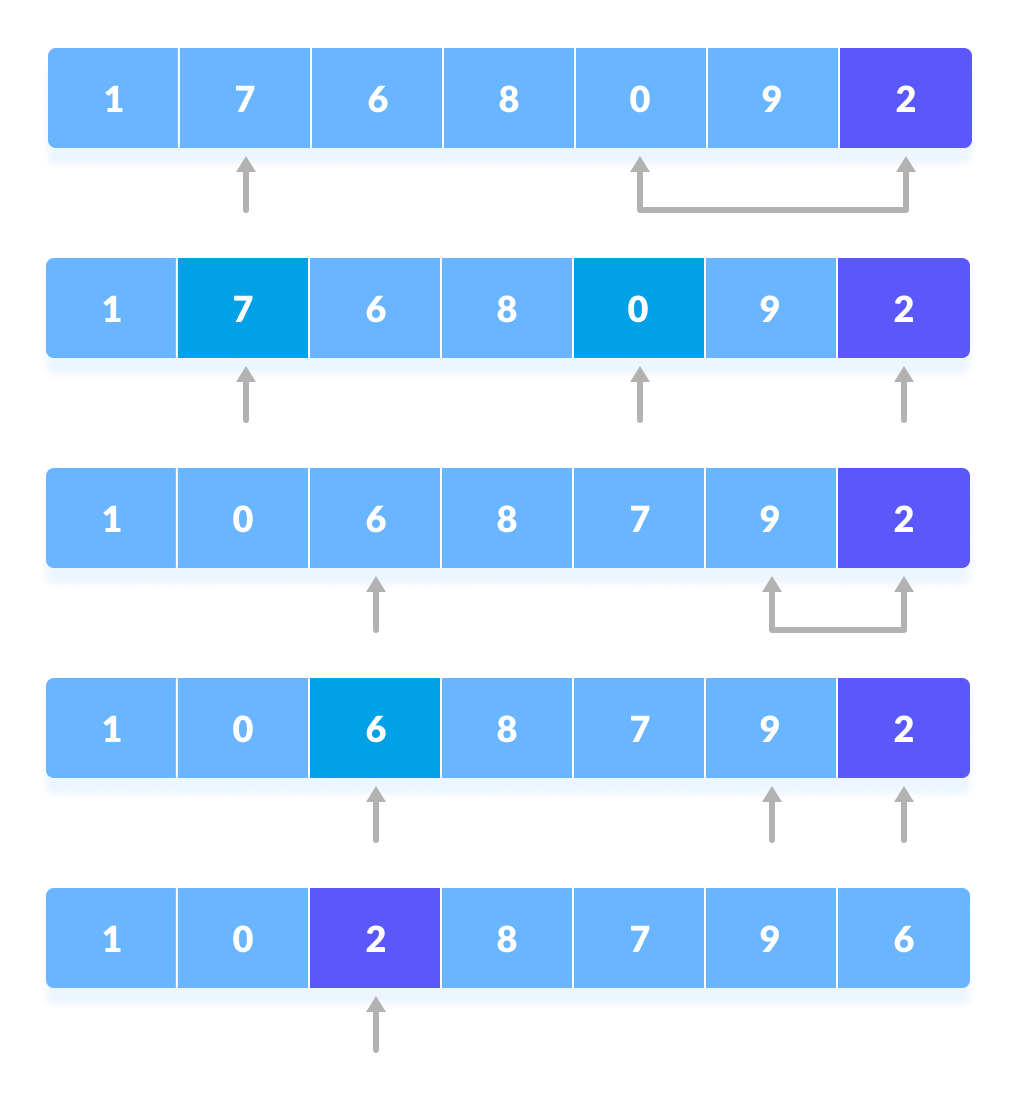
- A pivot element is chosen from the array. You can choose any element from the array as the pviot element.
Here, we have taken the rightmost (ie. the last element) of the array as the pivot element. - The elements smaller than the pivot element are put on the left and the elements greater than the pivot element are put on the right.
The above arrangement is achieved by the following steps.- A pointer is fixed at the pivot element. The pivot element is compared with the elements beginning from the first index. If the element greater than the pivot element is reached, a second pointer is set for that element.
- Now, the pivot element is compared with the other elements. If element smaller than the pivot element is reached, the smaller element is swapped with the greater element found earlier.
- The process goes on until the second last element is reached.
- Finally, the pivot element is swapped with the second pointer.
- A pointer is fixed at the pivot element. The pivot element is compared with the elements beginning from the first index. If the element greater than the pivot element is reached, a second pointer is set for that element.
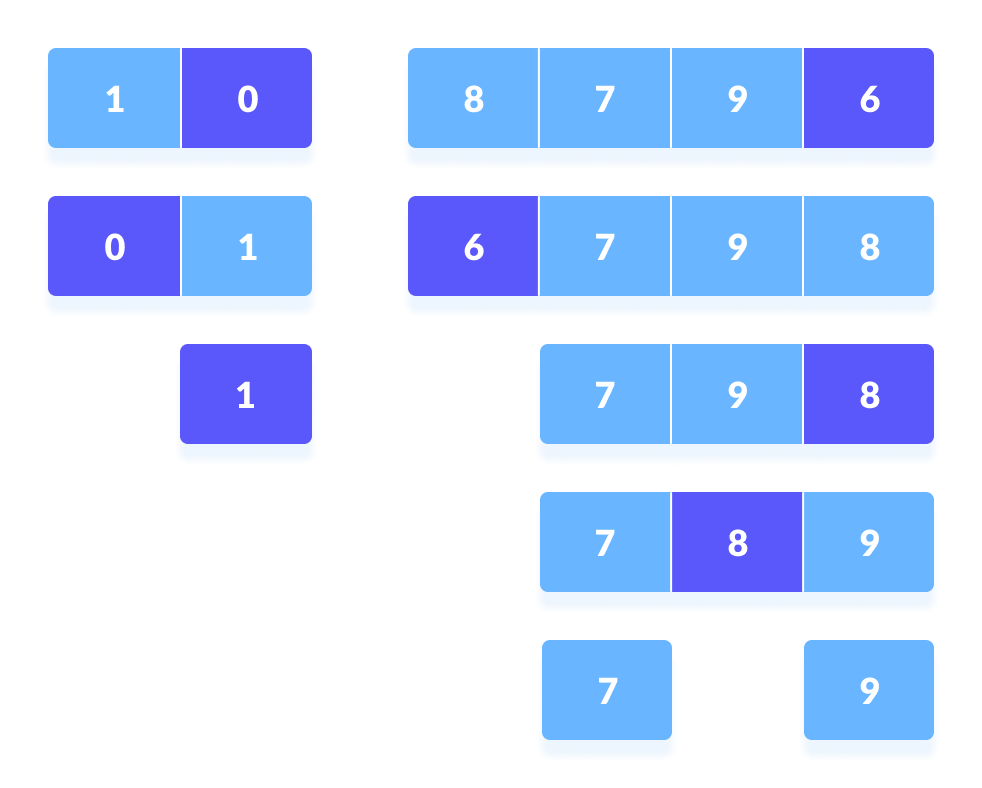
- Pivot elements are again chosen for the left and the right sub-parts separately. Within these sub-parts, the pivot elements are placed at their right position. Then, step 2 is repeated.
- The sub-parts are again divided into smallest sub-parts until each subpart is formed of a single element.Visit Our Channel for Similar tutorials
- At this point, the array is already sorted.
// Quick sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int partition(int array[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = array[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j < high; j++)
{
if (array[j] <= pivot)
{
i++;
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
void printArray(int array[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int data[] = {8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array in ascending order: \n");
printArray(data, n);
}


Comments
Post a Comment