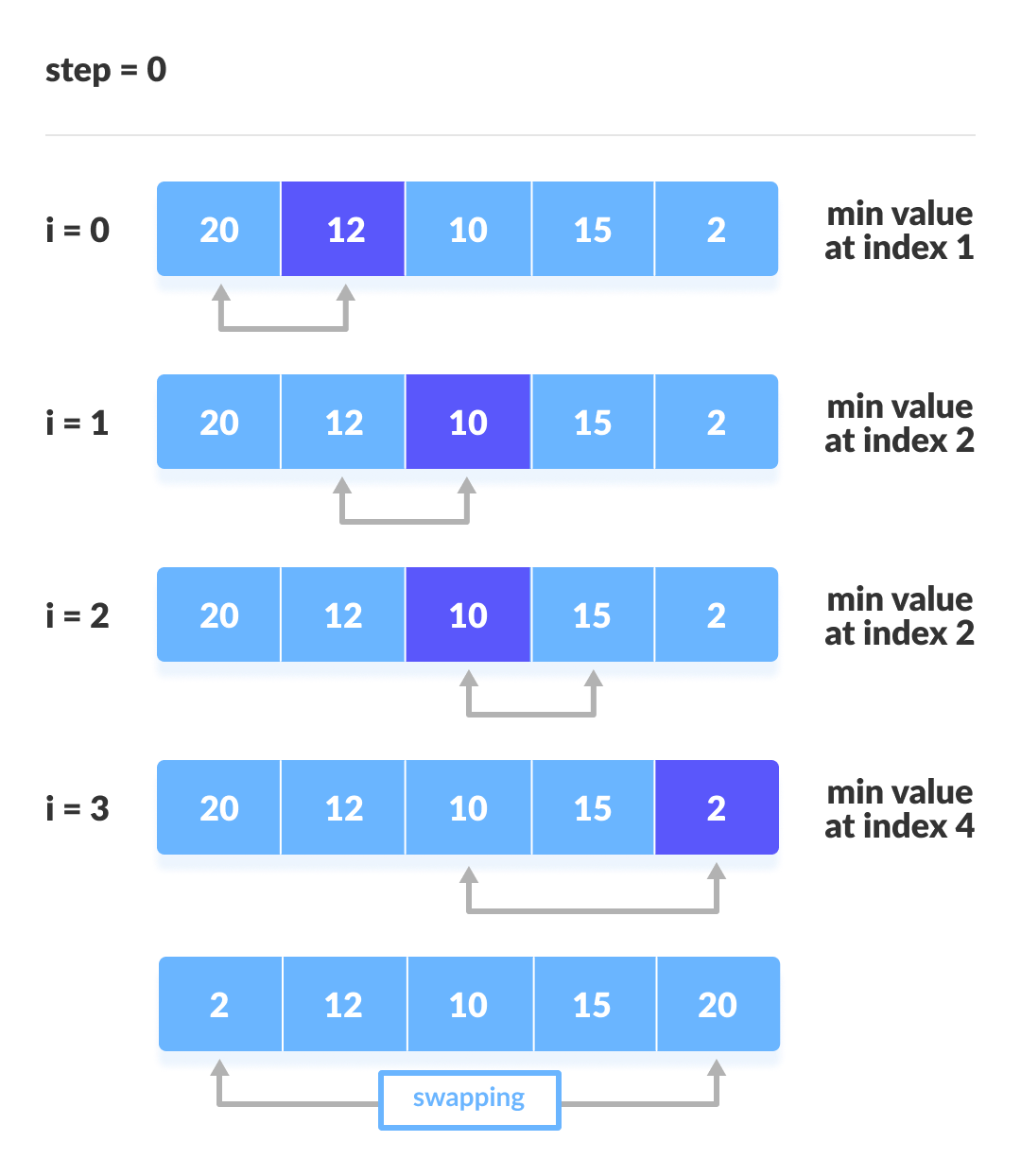
How Selection Sort Works?
- Set the first element as
minimum. - Compare
minimumwith the second element. If the second element is smaller thanminimum, assign second element asminimum.
Compareminimumwith the third element. Again, if the third element is smaller, then assignminimumto the third element otherwise do nothing. The process goes on until the last element. - After each iteration,
minimumis placed in the front of the unsorted list. - For each iteration, indexing starts from the first unsorted element. Step 1 to 3 are repeated until all the elements are placed at their correct positions.
// Selection sort in C Program
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void selectionSort(int array[], int size)
{
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++)
{
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++)
{
if (array[i] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = i;
}
swap(&array[min_idx], &array[step]);
}
}
void printArray(int array[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int data[] = {20, 12, 10, 15, 2};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
selectionSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted array in Acsending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}





Comments
Post a Comment